Complete Guide to Literature Reviews: Definition, Types, and Step-by-Step Writing Process

Literature reviews are foundational to quality research, but many students and researchers struggle with crafting effective ones. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about literature reviews—from definition to execution.
Literature Review Definition
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic or research question. It goes beyond a simple summary, providing an evaluation of the current state of knowledge in your field. A well-crafted literature review discusses published information, identifies patterns, gaps, and contradictions in the literature, and positions your research within this broader context.
Unlike an annotated bibliography that simply lists and summarizes sources, a literature review reorganizes and synthesizes information, often following thematic, methodological, or chronological patterns to create new insights about the topic.
Literature Review: The Essential Guide for Researchers
Literature reviews serve multiple crucial purposes in academic and research settings:
Contextualizing Your Research
They establish the background and framework for your research question, demonstrating how your work fits into the existing knowledge landscape.
Identifying Knowledge Gaps
By analyzing existing literature, you can pinpoint areas that need further investigation, justifying the significance of your study.
Building Theoretical Foundations
Literature reviews help you understand and develop theoretical frameworks that will guide your research.
Informing Methodology
Examining previous studies can provide insights into effective methodological approaches and help you avoid potential pitfalls.
Establishing Credibility
A thorough literature review demonstrates your expertise and familiarity with the field, building your credibility as a researcher.
Avoiding Duplication
By reviewing what's already been done, you ensure your research contributes new knowledge rather than simply repeating existing work.
Who Writes Literature Reviews?
Literature reviews are written across various disciplines but are especially common in the sciences and social sciences. They appear as:
- Sections within larger research papers, theses, or dissertations
- Standalone academic papers
- Preliminary research for professionals staying current in their fields
- Components of grant proposals or project plans

How to Conduct a Literature Review?
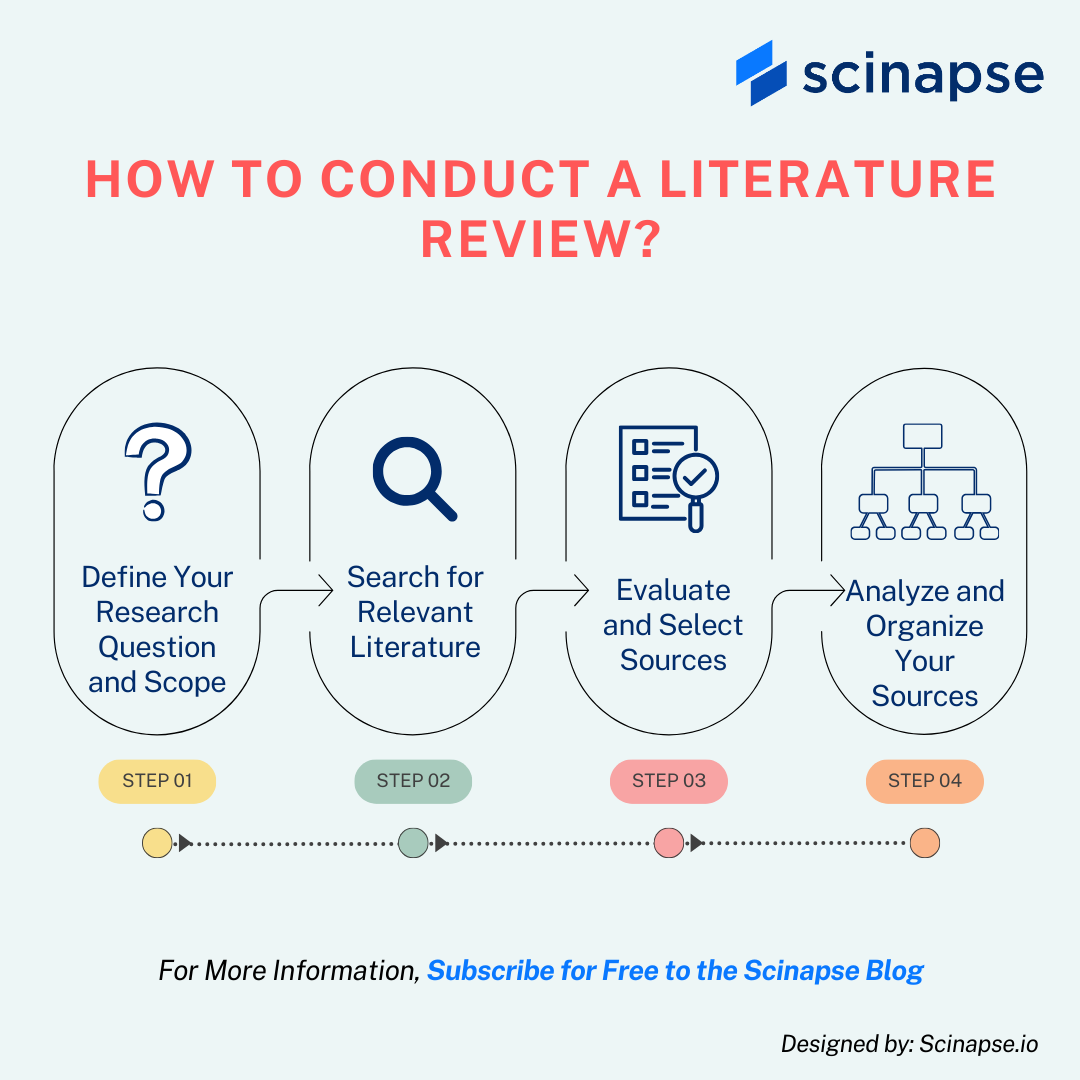
1. Define Your Research Question and Scope
Begin by clearly articulating what you want to investigate. Your research question should be specific enough to guide your search but broad enough to find sufficient literature. Consider:
- Time frame: Recent developments or historical overview?
- Geographical scope: Global or region-specific?
- Types of sources: Academic journals, books, reports, etc.?
2. Search for Relevant Literature
Developing an effective search strategy is crucial for finding high-quality, relevant sources. Here are approaches you can use:
Traditional Search Methods
- Library Databases: Access specialized academic databases through your institution's library
- Google Scholar: Search broadly across disciplines and publications
- Citation Tracking: Follow references from relevant papers to find connected research
- Journal Browsing: Explore top journals in your field for recent publications
While traditional search methods can be comprehensive, they often require significant time investment. Researchers may spend hours combing through databases, reviewing dozens of papers, and still struggle to find sources that align perfectly with their specific research focus.
AI-Powered Literature Review Tools
The evolution of literature search methods mirrors broader technological changes in academia. Traditional approaches required labor-intensive manual searches through physical libraries—time-consuming and geographically limited. The digital revolution brought online databases and search engines, substantially increasing access to scholarly works.
We are now witnessing another shift with AI-powered research tools that not only accelerate the search process but also provide novel insights through sophisticated analysis techniques.
For a quick literature search, choose Scinapse — an AI-powered academic search engine that helps discover relevant research papers, gain field insights, and track research trends. With access to approximately 250 million papers and a curated collection of 100 million quality-controlled publications, Scinapse tackles the overwhelming volume and complexity of academic literature search and analysis. It covers over 99% of Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) journals and integrates multiple public databases including MAG, Pubmed, Openalex, and Crossref, supplemented by web-crawled data.
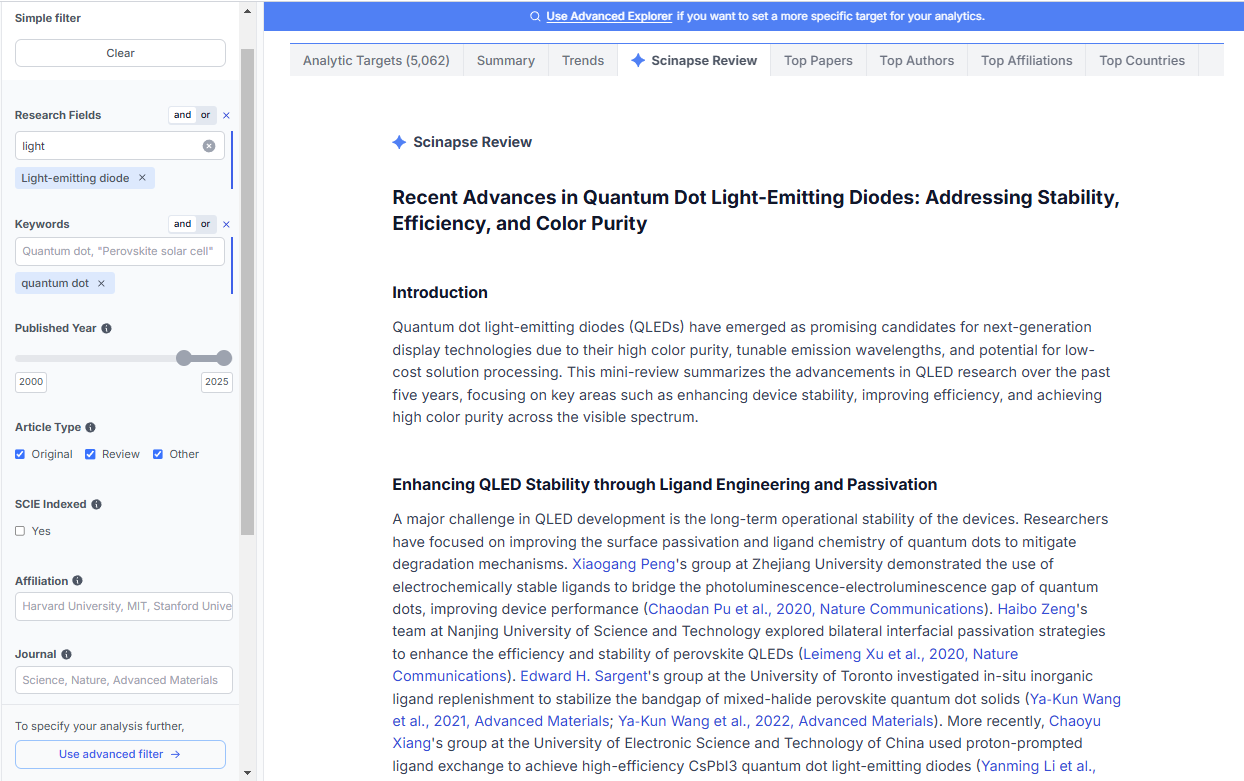
By entering a few keywords, researchers can generate a custom mini literature review tailored to their specific research scope. Instead of sorting through countless papers, you receive a concise summary of the most relevant insights from the past five years, allowing you to quickly grasp the research landscape.
Key benefits of using Scinapse for literature searches include:
- Customized AI Review Creation: Set your keywords, and the tool curates a personalized literature review based on your exact research focus
- Up-to-date Research Trends: Stay current with the most recent advancements, focusing on original research papers (not review articles)
- Efficient Grant Preparation: Quickly gather insights to strengthen research proposals by demonstrating awareness of current trends and gaps
- Time Savings: Bypass information overload by focusing only on the most relevant findings
When selecting an AI tool for a literature search, consider these important parameters:
- Research trends analysis capabilities
- Ability to filter papers by keywords
- Publication year range selection
- Institutional affiliations filtering
- Journal name filtering options
- Geographic/country filters
- Citation count information
- Journal impact factor data
These tools can be particularly valuable when starting a new research project or preparing grant applications, helping you identify research directions and explore related work efficiently.
3. Evaluate and Select Sources
Whether using traditional or AI-assisted methods, critically assess each potential source for:
- Relevance to your research question
- Credibility and authority of the author and publication
- Methodology and sample size
- Publication date and currency of information
- Citation frequency (how often others have referenced it)
4. Analyze and Organize Your Sources
As you review each source, consider:
- Key findings and arguments
- Methodological approaches
- Strengths and limitations
- How does it relate to other literature in your review
- Connections to your research question
Keep detailed notes on each source, including bibliographic information and your critical analysis.
How to Write a Literature Review? - Literature Review Format
1- Introduction
Your introduction should:
- Open with a statement about the broader topic's significance
- Clearly define the scope and purpose of your review
- Outline your organizational framework
- Explain why your review matters
- End with a thesis statement that previews your main argument
2- Body
The body of your literature review should be organized logically using one of these approaches:
- Chronological: Tracing the development of the topic over time
- Thematic: Organizing by themes or conceptual categories
- Methodological: Grouping studies by research methods used
For each section, provide:
- Summary of key findings
- Critical analysis of strengths and weaknesses
- Synthesis showing relationships between studies
- Identification of patterns, gaps, or contradictions
3- Conclusion
Your conclusion should:
- Summarize the main findings from the literature
- Highlight the contributions of your review
- Discuss implications for theory, practice, or policy
- Suggest directions for future research
- Emphasize the significance of your review
Writing Tips for an Effective Literature Review
- Maintain Your Voice: While discussing others' ideas, ensure your perspective remains clear and guides the review.
- Use Evidence: Support your interpretations with evidence from the literature.
- Be Selective: Focus on the most relevant points from each source rather than trying to include everything.
- Synthesize, Don't Just Summarize: Move beyond listing what each source says—draw connections between sources and identify patterns.
- Use Quotes Sparingly: Include direct quotes only when the author's original wording is particularly impactful or cannot be paraphrased effectively.
- Be Critical: Evaluate the quality, strengths, and limitations of each source.
- Avoid Plagiarism: Paraphrase carefully and cite sources accurately.
- Revise Thoroughly: Focus on presenting information concisely and clearly.
Common Organizational Patterns for Literature Reviews
1- Chronological Organization
A chronological approach traces the development of the topic over time, showing how the understanding of the issue has evolved. This works well for topics with clear historical development.
Example: In a review of climate change research, you might trace how scientific understanding progressed from early observations to current predictive models.
2- Thematic Organization
Thematic reviews organize sources around key themes or issues within the topic, regardless of when they were published. This approach helps highlight patterns and contradictions across the literature.
Example: A review of the effects of social media might have sections on psychological impacts, social relationships, and educational outcomes.
3- Methodological Organization
This approach groups studies based on the research methods used, comparing and contrasting different methodological approaches to the topic.
Example: A review of depression treatments might separate studies using quantitative clinical trials from qualitative studies of patient experiences.
Revising Your Literature Review
Revision is crucial for creating a polished literature review. Focus on:
- Organization: Check that your review follows a logical structure
- Clarity: Ensure your points are expressed clearly and concisely
- Flow: Create smooth transitions between sections
- Balance: Give appropriate attention to different aspects of the topic
- Consistency: Maintain consistent citation style and formatting
- Accuracy: Verify that you've represented sources correctly
Stay Updated
Literature reviews should reflect the current state of knowledge in your field. Consider:
- Setting up alerts in databases or AI tools for new publications on your topic
- Revisiting your literature review periodically if your research extends over a long period
- Documenting your search process thoroughly for reproducibility and future updates
Author: Uttkarsha B
- AI-Ethicist and STM Research & Publishing Expert
Never re-search again.
Scinapse is made by researchers for researchers.
Join the next generation of research at ⏯️ https://scinapse.io/
Pluto Labs
Pluto Labs helps researchers focus on their research by improving several inefficiencies in the academic research process. We offer data-driven insights from academic papers, allowing users to easily obtain review-level results for their desired range of papers.
https://pluto.im/



Comments ()